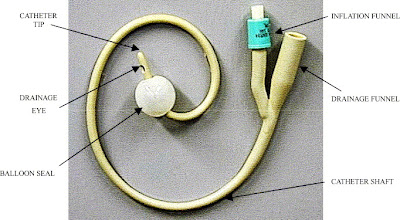
Nasogastric tube
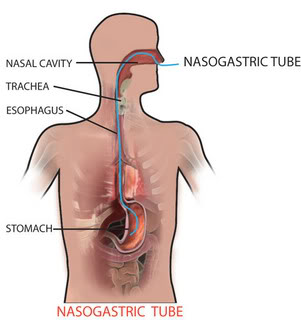
A nasogastric tube is a narrow bore tube passed into the stomach via the nose. It is used eg for decompression of intestinal obstruction.A wide bore tube is used if drainage is needed; otherwise, a finer bore tube is used. Fine bore feeding tubes (gauge less than 9) cause less discomfort and less risk of rhinitis, pharyngitis or oesophageal erosion. The use of a nasogastric tube is suitable for enteral feeding for up to six weeks. Polyurethane or silicone feeding tubes are unaffected by gastric acid and can therefore remain in the stomach for a longer period than PVC tubes, which can only be used for up to 2 weeks. For long-term enteral feeding, the use of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is associated with improved survival, better toleration by the patient and lower incidence of aspiration. Contra-indications The nasogastric feeding route is not suitable for all patients, including those with: High risk of aspiration Gastric stasis Gastro-oe